# How is Dew Point Calculated?
## Understanding Dew Point
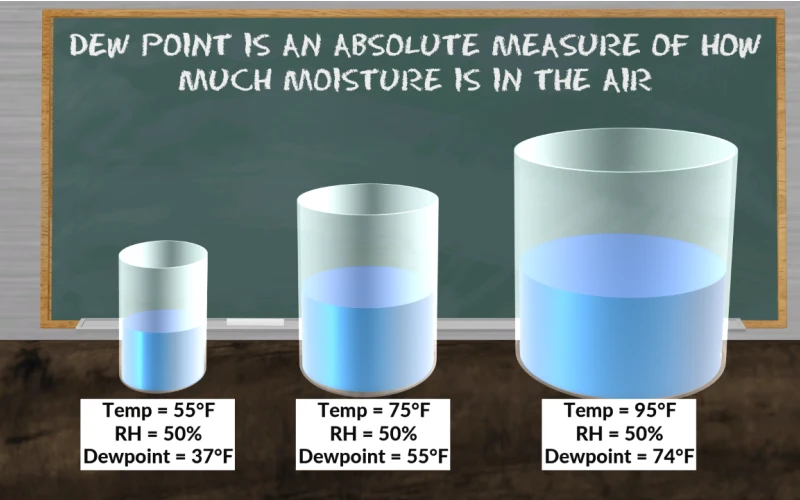
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, frost, or fog. It’s a crucial measurement in meteorology, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. Understanding how dew point is calculated helps in predicting weather patterns and maintaining optimal environmental conditions.
## The Science Behind Dew Point Calculation
The calculation of dew point involves several atmospheric variables and mathematical formulas. Here’s how it works:
### Key Variables Needed
To calculate dew point, you’ll need to know:
– Air temperature (in °C or °F)
– Relative humidity (percentage)
– Atmospheric pressure (though often assumed constant for simpler calculations)
### Basic Calculation Method
The most common method for calculating dew point uses the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– a and b are Magnus coefficients (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C for temperatures above 0°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH/100)
– T is the temperature in °C
– RH is relative humidity (as a percentage)
– ln is the natural logarithm
## Step-by-Step Calculation Example
Let’s calculate the dew point for air at 25°C with 50% relative humidity:
1. Calculate α(T,RH):
α = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(0.50)
α = 431.75/262.7 + (-0.6931)
α ≈ 1.6436 – 0.6931 ≈ 0.9505
2. Calculate dew point:
Td = (237.7 × 0.9505)/(17.27 – 0.9505)
Td ≈ 225.93/16.3195 ≈ 13.84°C
## Simplified Approximation
For quick estimates, you can use this simplified formula when relative humidity is above 50%:
Td ≈ T – (100 – RH)/5
Using our previous example:
Td ≈ 25 – (100 – 50)/5 = 25 – 10 = 15°C
While less precise, this approximation gives a reasonable estimate for many practical purposes.
## Practical Applications of Dew Point
Understanding dew point calculations has numerous applications:
### Weather Forecasting
Meteorologists use dew point to predict:
– Likelihood of precipitation
– Fog formation
– Comfort levels (higher dew points feel more humid)
### Industrial Processes
Many industries monitor dew point to:
– Prevent condensation in compressed air systems
– Control drying processes
– Maintain optimal conditions in manufacturing
### Building Science
HVAC professionals calculate dew point to:
– Prevent mold growth
– Avoid condensation on windows and walls
– Design proper ventilation systems
## Tools for Dew Point Calculation
While manual calculations are educational, most professionals use:
– Psychrometric charts
– Online dew point calculators
– Specialized meteorological instruments
– HVAC system sensors and controllers
## Factors Affecting Dew Point Accuracy
Several factors can influence dew point calculations:
– Altitude (affects air pressure)
– Temperature measurement precision
– Humidity sensor accuracy
– Local atmospheric conditions
Understanding these variables helps in obtaining more accurate dew point measurements for specific applications.
## Conclusion
Dew point calculation is a fundamental meteorological process that combines temperature and humidity measurements. While the mathematical formulas may seem complex at first, understanding the basic principles allows for better interpretation of weather data and environmental conditions. Whether you’re a weather enthusiast, HVAC technician, or industrial engineer, knowing how to calculate and interpret dew point values is an invaluable skill for predicting and controlling moisture in the air.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated
